Navigating Food Allergies: Understanding Ingredients and Alternatives
Food allergies affect millions of people around the world, and the number continues to rise. For those who have food allergies, it can be a daunting task to navigate through grocery aisles, restaurant menus, and even family meals. Understanding ingredients and finding alternatives are key to managing food allergies and ensuring a safe and healthy diet. In this article, we will explore how to navigate food allergies by understanding ingredients and discovering alternatives.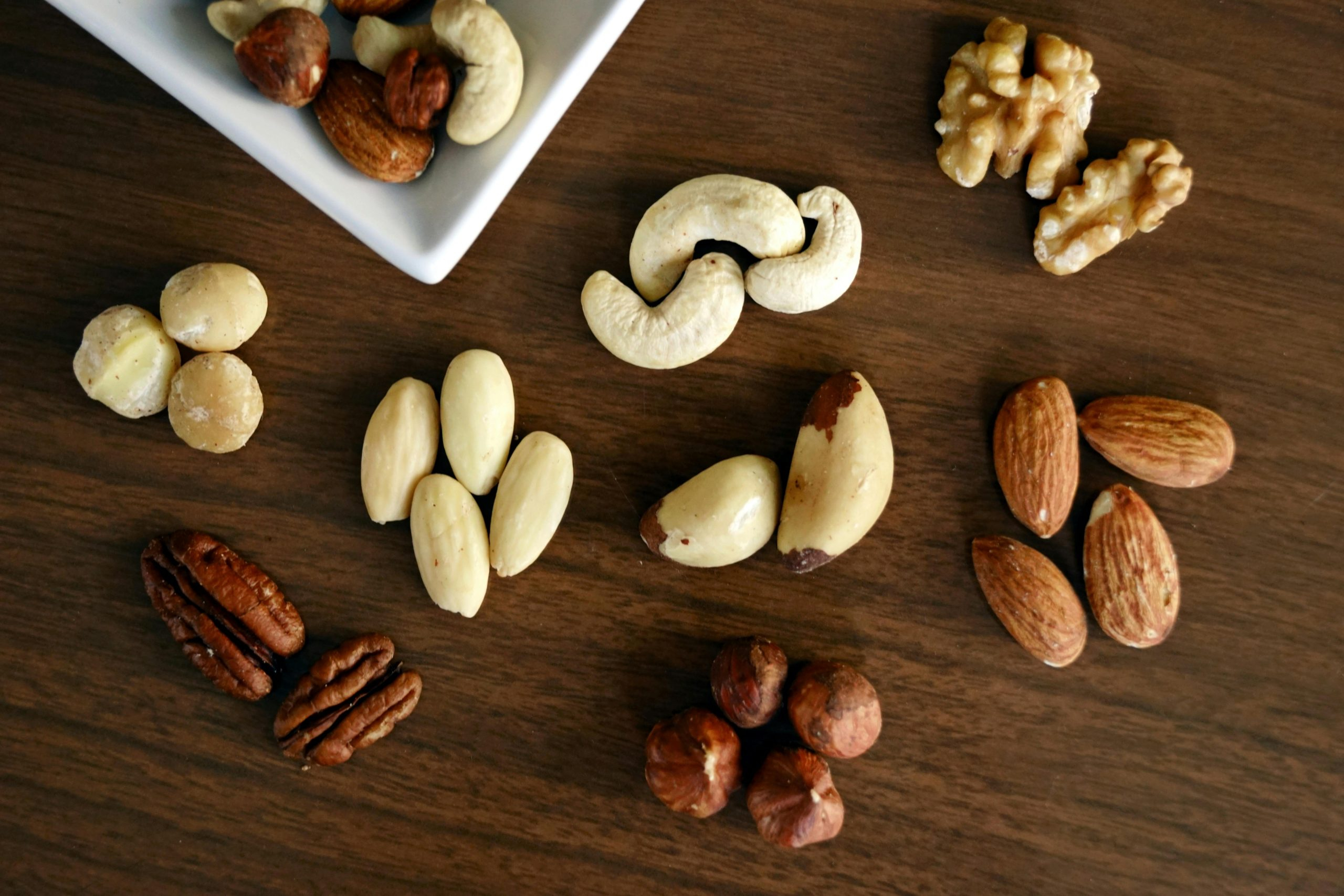
The Basics of Food Allergies
First, let’s start with the basics. A food allergy is an immune system response to a particular food, causing a range of symptoms, from mild discomfort to life-threatening reactions. The most common allergens include peanuts, tree nuts, milk, eggs, soy, wheat, fish, and shellfish. However, any food can cause an allergic reaction, and some people may have allergies to multiple foods.
It is essential to understand that food allergies are different from food intolerances. Food intolerances are often caused by the body’s inability to digest certain components in the food, such as lactose in dairy. Food allergies, on the other hand, involve the immune system and can trigger a severe reaction even in small amounts.
Reading Labels and Avoiding Allergens
The first step in navigating food allergies is to become an expert at reading food labels. Food manufacturers are required to list common allergens on their product labels. Look for keywords like “contains,” “may contain,” or “made in a facility that also processes” followed by the allergen. It is also essential to note that labels can change, so it is crucial to check them every time you buy a product.
When shopping for fresh produce, it is essential to check with the store or farmer’s market about the growing and handling practices. Cross-contamination can occur when the same equipment or storage containers are used for different products. Additionally, it is crucial to wash fruits and vegetables thoroughly before consuming.
Understanding Ingredients
Many food ingredients can have different names and forms, making it challenging to spot potential allergens on a food label. Here are some common allergens and their alternative names:
Milk
Aside from the obvious “milk” ingredient, dairy can also be found under names such as “whey,” “casein,” or “lactose.” Non-dairy alternatives to milk include almond, soy, oat, or rice milk.
Eggs
Eggs can be disguised as “albumin,” “globulin,” “lecithin,” or even as a binder in “mayonnaise.” Some alternatives to eggs include flaxseed, chia seeds, or commercially available egg substitutes.
Wheat
Wheat can be found in many processed foods, such as bread, pasta, and cereals. Alternative grains like quinoa, rice, and oats are safe for those with wheat allergies. However, it is essential to check if they are processed in a facility that also handles wheat.
Tree Nuts
Tree nuts can be listed under various names, such as “almond flour,” “cashew butter,” or “hazelnut spread.” Sunflower seed butter, pumpkin seed butter, or tahini are safe alternatives to nut butter.
Finding Alternatives
Living with food allergies does not mean sacrificing taste and variety in your diet. The good news is that many alternatives can be found easily, either in natural or specialty food stores. Here are some options to consider:
Flours
If you have a wheat or gluten allergy, there are plenty of flours and starches to choose from, such as rice, almond, coconut, or tapioca flour. These can be used to make bread, cakes, or even pizza crust.
Sweeteners
Instead of using traditional white sugar, there are many natural alternatives, such as honey, maple syrup, or coconut sugar. For those with a corn allergy, agave nectar or stevia can be used.
Plant-Based Milk
Animal milk alternatives, such as almond, coconut, or soy milk, are available in most grocery stores. These are perfect for people with dairy allergies or those following a plant-based diet.
Baking Substitutes
There are plenty of options to replace eggs in baking, such as applesauce, mashed bananas, or even a mixture of water, oil, and baking powder.
Nut Butter Alternatives
For people with nut allergies, there are many seed butter alternatives, such as sunflower seed or pumpkin seed butter. You can also make your seed butter at home by blending seeds with oil and a sweetener.
In Conclusion
Food allergies can be challenging to navigate, but with the right knowledge, it is possible to manage them and enjoy a healthy and diverse diet. Always read labels, understand ingredients, and experiment with alternatives to find what works best for you. With the increasing number of food allergies, there are also many resources and support groups available to help you along the way. With a little bit of effort and creativity, you can safely and deliciously navigate through food allergies.